
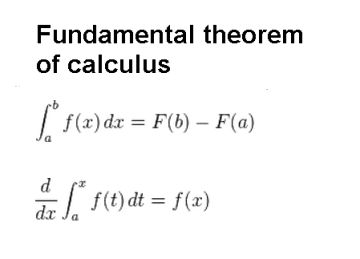
There are common functions and rules we follow to find the integration. Use the Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, if needed, to calculate each the derivatives expressed in Exercises 3548. Double integral of function f (x, y) over the rectangular plane S in the xy plan is expressed by S f ( x, y ) d A l i m j, k > I 1 m j. It is represented as \(\int\limits_a^b \) Then, for all x in a, b, we have m f(x) M.

Proof Since f(x) is continuous on a, b, by the extreme value theorem (see Maxima and Minima ), it assumes minimum and maximum values m and M, respectivelyon a, b. It is represented as ∫f(x)dxĭefinite integrals: The integrals that have upper and lower limits. (5.15) This formula can also be stated as b af(x)dx f(c)(b a).
Indefinite integrals: The integrals do not have any upper and lower limits. The integrals are classified into 2 types: 1. Integration is defined as the reverse process of differentiation. There are common functions and rules we follow to find derivatives The process of finding derivatives is called differentiation. The symbol dy and dx are called differentials. It means that the function is the derivative of y with respect to the variable x. Enter the two-variable function into the input box. The First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus' and 'Primitive Functions and the Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.' §5.1 and 5.3 in Calculus, 2nd ed. The derivative of a function is represented by f '(x). How does the Double integration Calculator work Select the option first, definite or indefinite. It is read as “the limit of a function of x equals A as and when x approaches a.” The limit formula to calculate the derivative of a function is: Limits are used as a way of making approximations used in the calculation as close as possible to the actual value of the quantity.
#Second theorem of calculus calculator how to
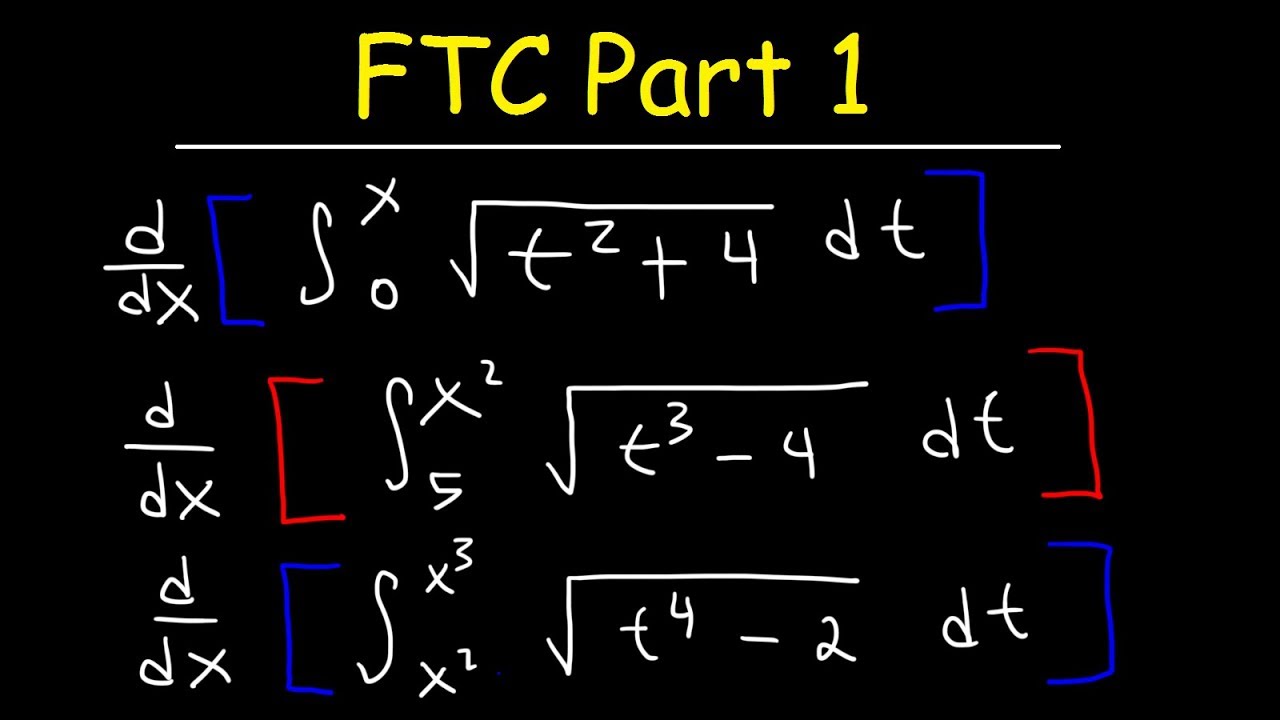
How to Find the limits, derivatives, indefinite integrals and definite integrals?
Step 4: Click on the "Reset" button to clear the fields and enter the different functions. Step 3: Click on the "Calculate" button to find the values of limits, derivatives, indefinite, and definite integrals. Step 2: Enter the function in the given input boxes. Step 1: Choose a drop-down list to find the value of limits, derivatives, indefinite, and definite integrals. Step 2: Now click the button Solve to get the roots. Let s(t) s ( t) represent the height of the water balloon above the ground at time t, t, and note that s s is an antiderivative of v. The procedure to use the 2nd degree equation calculator is as follows: Step 1: Enter the coefficients A, B, C in the input field. Please follow the steps below on how to use the calculator: It turns out that the instantaneous velocity of the water balloon is given by v(t) 32t+16, v ( t) 32 t + 16, where v v is measured in feet per second and t t is measured in seconds. Using the second fundamental theorem of calculus on g(x). NOTE: Enter the function with respect to x only. C Use the Calculate Zero function on your calculator to find the first positive x-intercept. It is concerned with the rates of changes in different quantities, as well as with the accumulation of these quantities over time. 'Cuemath's Calculus Calculator' is an online tool that helps to calculate the value of limits, derivatives, indefinite, and definite integrals. Cuemath's online Calculus Calculator helps you to calculate the value of the derivatives in a few seconds. What is calculus Calculus is a branch of mathematics that deals with the study of change and motion. State both parts of the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. "Fundamental Theorems of Calculus." From MathWorld-A Wolfram Web Resource.Calculus is one of the most important branches of mathematics, that deals with continuous change. The rate of production of these calculators after t weeks is 90. Referenced on Wolfram|Alpha Fundamental Theorems of Variable Calculus with Early Transcendentals. "The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus along Curves." §2.1.5 Of Calculus" and "Primitive Functions and the Second Fundamental TheoremĢnd ed., Vol. 1: One-Variable Calculus, with an Introduction to Linear Algebra. 'The Derivative of an Indefinite Integral.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
